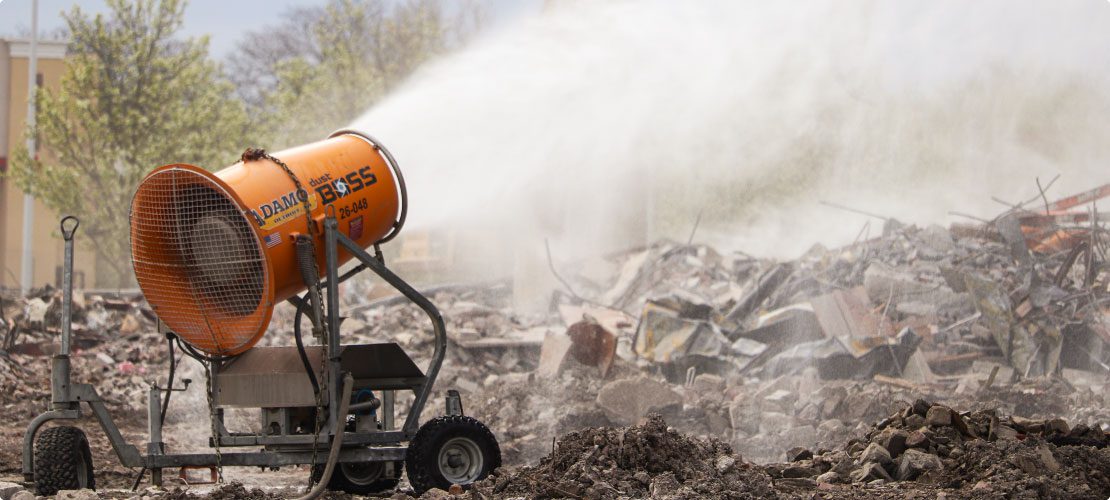
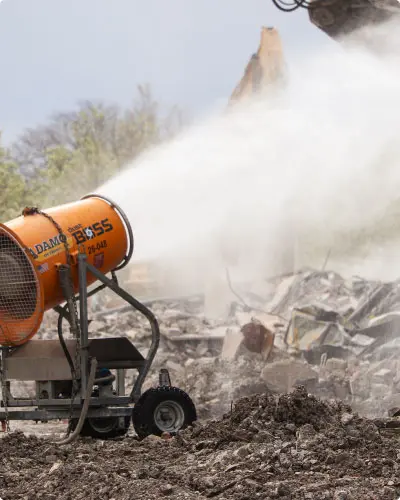
In 2023, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) announced new rules regarding Respirable Crystalline Silica (RCS) dust emissions, marking a major adjustment to how to address the top silica dust exposure hazards in the workplace from ports to mines to construction sites.[1] This quickly follows a similar announcement by the U.S. Mining Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) Chief of Health, Gregory Meikle, regarding rules changes in mines, quarries, and mineral extraction. Both concluded that an integral part of controlling RCS emissions is the “Implementation of properly designed wet spray systems.” [2]
MSHA committed to reviewing silica regulations in response to requests from generations of miners in West Virginia suffering from “Black Lung” (aka silicosis or pneumoconiosis). OSHA’s reaction to MSHA’s findings shows that chronic disease caused by RCS is not just an old disease from the industrial revolution. It is an ongoing health issue that weaves across the entire bulk handling industry and, according to OSHA, can also cause other chronic health issues such as COPD, kidney disease, and lung cancer. [3] The organization estimates that 2.3 million workers are exposed to silica dust annually.
Why is RCS so pervasive? Because 97% of the earth’s crust contains some silica and the substance alone constitutes 26% of the earth’s crust by weight. [4] Although it is represented in high concentrations in coal mines, it also is present in limestone, clay, slate, sand, etc. These substances are found in the building blocks of society from concrete to microchips, and as the table below shows, there is no industry that is untouched by these new rules.
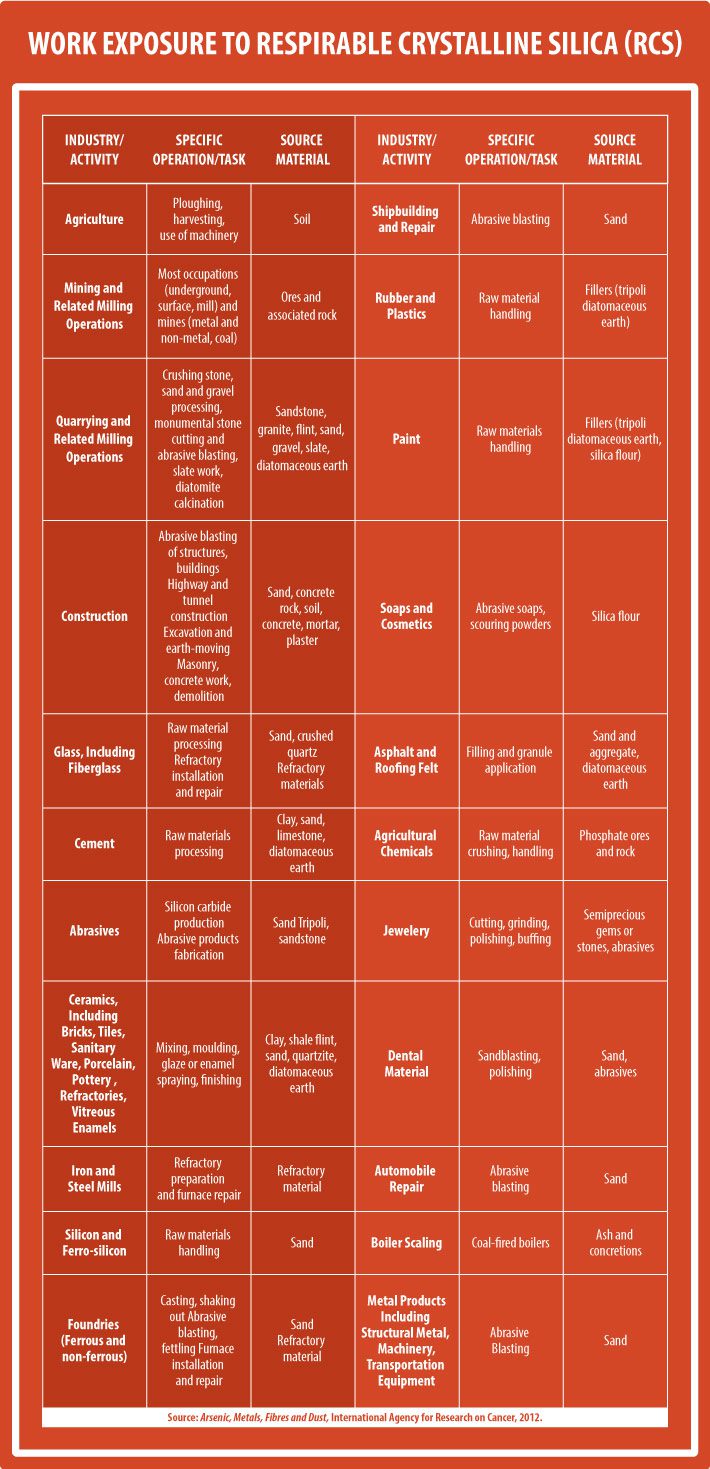
Table 1 – Silica Dust Exposure by Work Industry and Activity
WHY IS CRYSTALLINE SILICA DANGEROUS?
Silica crystals are nearly invisible to the naked eye due to their microscopic size, so even when the air seems clear, they can be present in relatively high concentrations. RCS of a Particulate Matter (PM) measuring ≤10 microns (μm) – about the size of bacteria -- can penetrate the body’s natural defenses (mucus membranes, cilia, etc.), reaching deep into the lungs. The small particle size allows these dust emissions to travel long distances on ambient air currents.
Although personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respirator masks are mandated by employers, observation and study over the years have revealed that PPE is often not adequate. First, wearing PPE every day over entire shifts can be uncomfortable and unsustainable for employee morale and retention. PPE can be worn incorrectly and filters can be left unchanged beyond equipment specifications. Due to the invisible nature of the particulate, workers may also be unaware of the lingering RCS and take off their safety equipment, thinking the air is safe.
This is why rules are being changed. Although PPE is still recommended where it makes sense, the top recommendation is water spray systems with the ability to capture airborne particulates. After field-testing, many bulk handlers will attest that the most effective method for controlling airborne emissions are industrial misting cannons.
READY FOR A QUOTE?
Talk to a dust control specialist and get a quick quote for your project.
OSHA SILICA DUST RULES
A division of the Department of Labor, OSHA can enter, inspect, report, fine, and halt operations at any workplace for purposes of worker safety without prior notice. Inspectors test the levels of dust by microgram (µg) per cubic meter (m3) of air over a Time Weighted Average (TWA). The Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) is the airborne concentration and volume of RCS the employee is exposed to over the TWA.
OSHA RCS STANDARDS BY INDUSTRY:
- General industry - 29 CFR 1910.1053 - Employee exposure to respirable crystalline silica will remain below 25 micrograms per cubic meter of air (25 µg/m3) as an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) under any foreseeable conditions. PEL = 50 µg/m3.
- Shipyards/Ports - (29 CFR 1915.1053) – Same as above. PEL = 50 µg/m3.
- Construction/Demolition - (29 CFR 1926.1153) – Standards are separated by the dust generating activity. Click the link then refer to TABLE 1 for more details.
CONTROLLING AIRBORNE RCS
The U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) published an extensive study in 2018 on the most effective method to address airborne particulates, specifically explosive coal dust in longwall mining operations.[5] Researchers concluded that widely distributed atomized mist droplets presented the highest capture rate of particulates <75 µm.For water to effectively suppress airborne dust, the droplets must be roughly equal in size to the particles. The reason for this is the “slipstream effect.” Hoses create water droplets 200 - 10,000 µm in size as compared to atomized mist, which ranges from 50 – 200 µm. Larger than 200 µm, droplets are unable to linger in the air or collide with dust particles. Due to the mass of larger droplets, they fall and form air currents around them. Like wind traveling around an airplane wing giving it lift, large droplets cause the same effect. When the tiny particles encounter the larger droplets, they get caught in the slipstream, which diverts them away from the droplet rather than being absorbed.
[Figure 1]
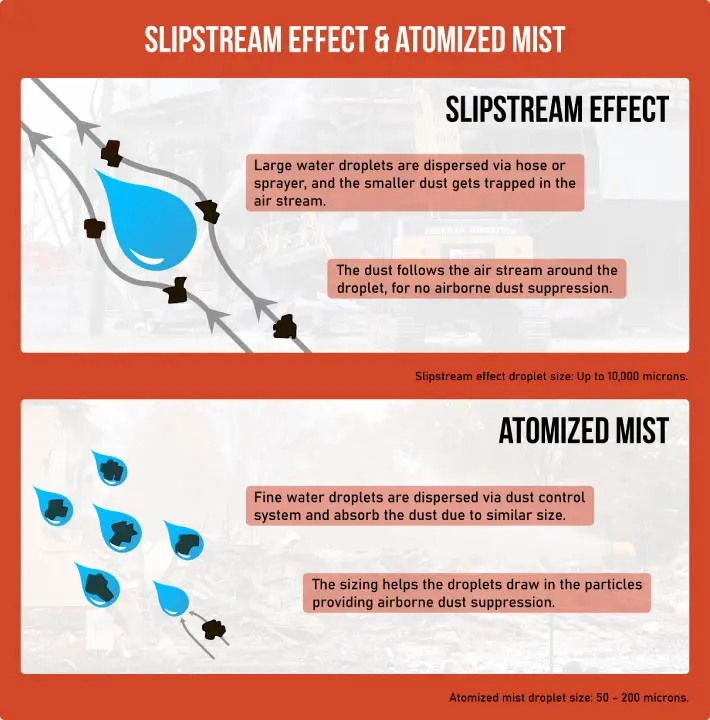
Figure 1 – Particle's reaction to the slipstream effect.
HOW DO MIST CANNONS WORK?
Industrial mist cannons employ a cone-shaped barrel with atomizing nozzles in the front and a powerful fan in the back, protected by a mesh safety grate. They can be direct-wired or powered by a generator set. Water is supplied by a 1.5 in. (38.10 mm) hose with a cam-and-groove quick disconnect female coupling (sizes may vary depending on the size of the equipment and the available water sources). It is run through an in-line 30 mesh 595 micron filter system to remove impurities that can clog nozzles, then to a booster pump to increase pressure – which is why the cannon only initially requires 10PSI (0.69 BAR) of constant pressure to operate. The pressurized water is pumped to a brass or stainless steel manifold with as many as 38 nucleating nozzles. The nozzles fracture the water into a fine atomized mist.
The powerful rear fan directs air through the cannon ring, propelling the mist up to 100 m (328 ft) and covering as much as 280,000 square feet with a single machine using a 359º oscillator and 0-50º vertical adjustment.
The mist raises the humidity in the coverage area where droplets float on ambient air currents with the dust particles, creating a zone where dust has a low likelihood of remaining airborne and escaping.
OTHER METHODS OF RCS CONTROL AND COMPLIANCE
Monitoring and controlling dust emissions that are too small to see can be difficult. If the silica dust exposure is not able to be controlled by a mist cannon system, then OSHA gives very general instructions regarding methods of compliance, advising companies to:
- Use engineering controls - These include isolating dust in sealed chute systems and dust collectors, and/or using water-based atomized suppression systems.
- Provide respirators – Compliance cannot be achieved by respirators alone but should be used in areas where engineering controls cannot adequately limit exposure.
- Limit worker access to high exposure areas – This is done by varying staff assignments throughout the day.
- Create a dust management plan (DMP) – Have it available along with monitoring results.
- Offer medical exams to highly exposed workers – Review the regulation for compliance details.
- Train workers on silica risks and how to limit exposures – Workers should be able to identify to OSHA inspectors the dust control supervisor and the compliance details when asked.
CHOOSING A MIST CANNON
Regulators recommend water systems for mitigating airborne dust from the top silica dust hazards because it’s a viable and cost effective method for most bulk handlers, recyclers, construction/demolition contractors, ports, and mining/quarry operators to stay compliant.
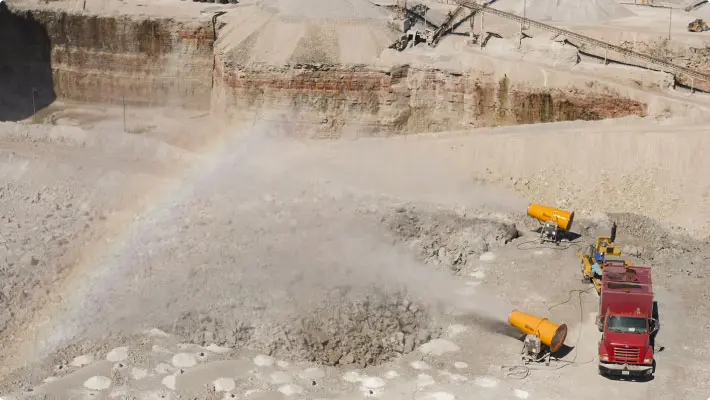

When seeking a compliant means to control airborne dust, there are a few considerations to keep in mind.
- What are the needs of your operation? Investigate the greatest sources of dust, then tackle those first. Once the larger sources are addressed, it is easier to identify smaller sources, monitor them, and seek affordable smaller scale solutions.
- How large is the site and who is affected? If there is a nearby community or businesses that are being adversely affected by dust, consider prevailing winds, and common seasonal patterns. Cannons like the DB-60 Surge are rugged and able to operate in varying conditions. Also, consider moving storage piles and dust causing operations away from the site line and positioning mist cannons appropriately to attack airborne dust before it leaves the site.
- Do you need a static or mobile dust control solution? Static operations like a slag recycler or coal terminal may choose to have tower mounted cannons because the storage area is established. A quarry, though it doesn’t move like a demolition contractor from project to project, may choose a mobile option since the working face and winds are ever-changing. Think about what you need now, then buy a DustBoss that provides room for your operation to grow.
- Do you need to buy or rent a mist cannon? – It’s hard to predict the needs of each project during certain seasons. Having a DustBoss on hand for each project or excavator and then supplementing them with rentals as needed is an economical option.
- What is your water and power availability? Many sites may be so large that availability to power or water might be a challenge. The DustBoss Fusion allows operators to power the unit with a generator set. Since the unit is autonomous, attaching it to a tanker truck offers long periods of operation without disruption due to power and water demands.
- What is the warranty? The standard DustBoss warranty for most models is 3 years or 3,000 hours, one of the longest in the industry.
DUST AND COMPLIANCE
Throwing labor at a dust solution can put workers in the way of machinery and puts them right where the dust is being created. If the OSHA inspector has them wear a personal dust monitor, then ironically, there is a chance that the person assigned to control dust for the site could be the source of a dust violation. With a thorough DMP and effective DustBoss technology, compliance with MSHA and OSHA dust regulations is the outcome.
Contact us for an on-site inspection of your operation. Our dust control experts will be able to identify and recommend solutions to most dust generating activities.
START PREVENTING SILICA DUST EXPOSURE TODAY!
Get a FREE quote to mitigate silica emissions and consult with a dust control expert now!